Form basics¶
Create / Edit form¶
Just inherit from cms.form to add a form for your model. Quick example for partner:
class PartnerForm(models.AbstractModel):
_name = 'cms.form.res.partner'
_inherit = 'cms.form'
_form_model = 'res.partner'
_form_model_fields = ('name', 'country_id')
_form_required_fields = ('name', 'country_id')
In this case you’ll have form with the following characteristics:
- works with
res.partnermodel - have only
nameandcountry_idfields - both fields are required (is not possible to submit the form w/out one of those values)
Here’s the result:
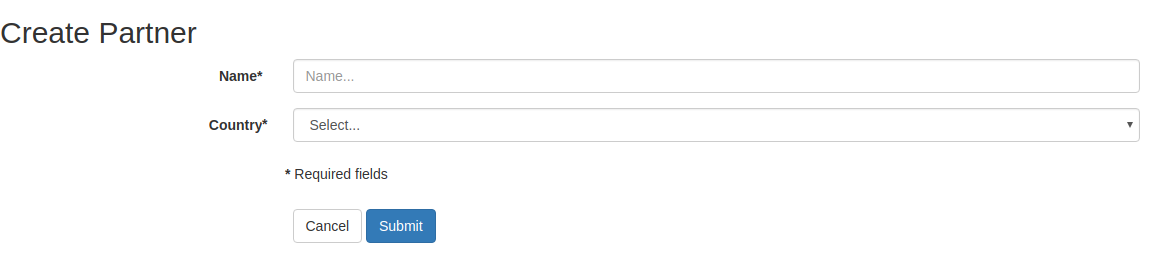
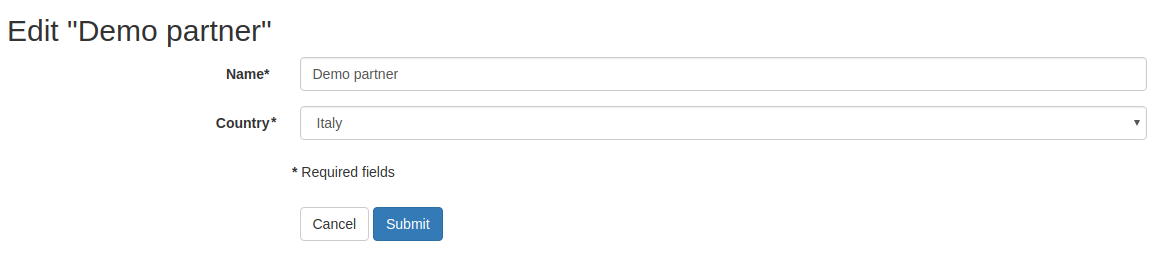
The form will be automatically available on these routes:
/cms/create/res.partnerto create new partners/cms/edit/res.partner/1edit existing partners (partner id=1 in this case)
NOTE: default generic routes work if the form’s name is cms.form. + model name, like cms.form.res.partner.
If you want you can easily define your own controller and give your form a different name,
and have more elegant routes like `/partner/edit/partner-slug-1.
Take a look at cms_form_example module.
By default, the form is rendered as an horizontal twitter bootstrap form, but you can provide your own templates of course.
By default, fields are ordered by their order in the model’s schema. You can tweak it using _form_fields_order.
Form with extra control fields¶
Imagine you want to notify the partner after its creation but only if you really need it.
The form above can be extended with extra fields that are not part of the _form_model schema:
class PartnerForm(models.AbstractModel):
_name = 'cms.form.res.partner'
_inherit = 'cms.form'
_form_model = 'res.partner'
_form_model_fields = ('name', 'country_id', 'email')
_form_required_fields = ('name', 'country_id', 'email')
notify_partner = fields.Boolean()
def form_after_create_or_update(self, values, extra_values):
if extra_values.get('notify_partner'):
# do what you want here...
notify_partner will be included into the form but it will be discarded on create and write.
Nevertheless you can use it as a control flag before and after the record has been created or updated
using the hook form_after_create_or_update, as you see in this example.
Form with fieldsets and tabs¶
You want to group fields into meaningful groups. You can use fieldsets:
class PartnerForm(models.AbstractModel):
_name = 'cms.form.res.partner'
_inherit = 'cms.form'
_form_model = 'res.partner'
_form_model_fields = ('name', 'country_id', 'email')
_form_required_fields = ('name', 'country_id', 'email')
_form_fieldsets = [
{
'id': 'main',
'title': 'Main',
'fields': [
'name',
'email',
],
},
{
'id': 'secondary',
'title': 'Secondary',
'fields': [
'country_id',
'notify_partner',
],
},
]
notify_partner = fields.Boolean()
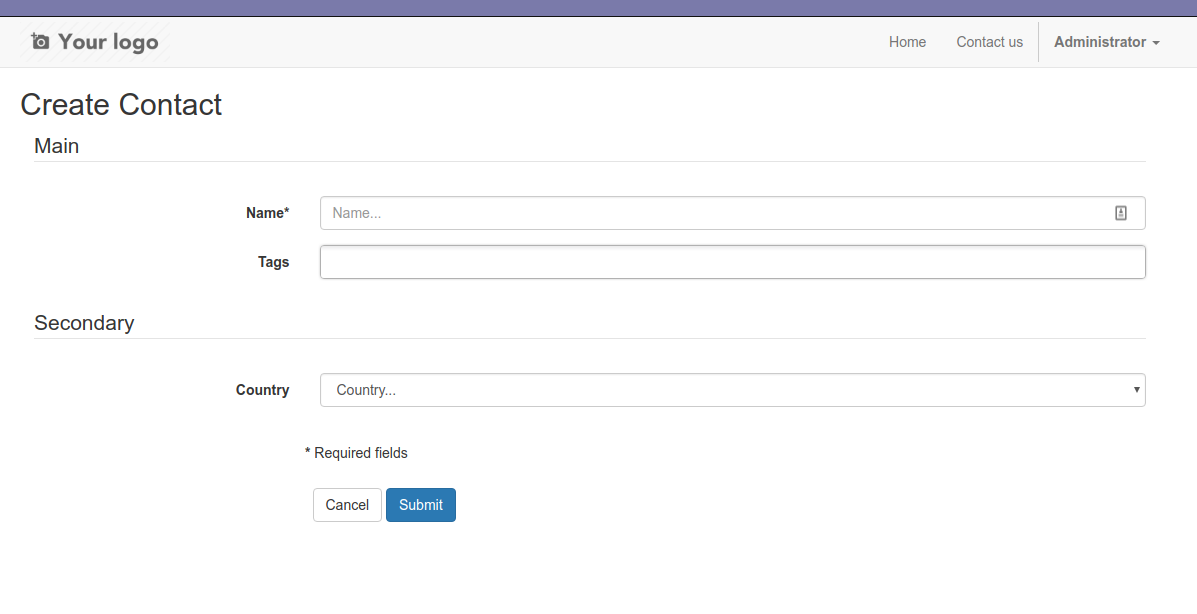
If you want fieldsets to be displayed as tabs, just override this option:
class PartnerForm(models.AbstractModel):
_name = 'cms.form.res.partner'
_inherit = 'cms.form'
_form_fieldsets = [...]
_form_fieldsets_display = 'tabs'
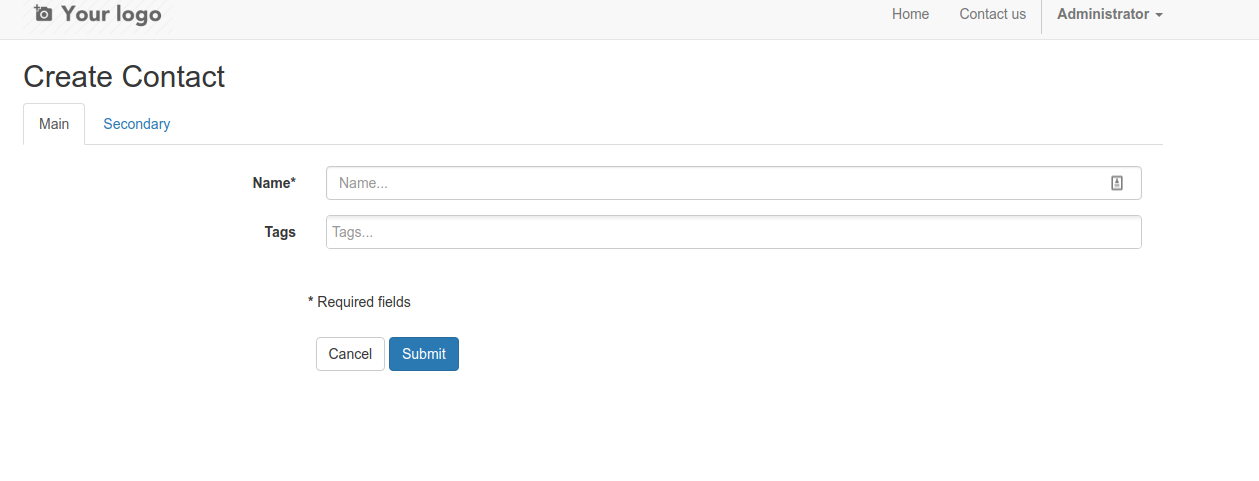
Search form¶
Just inherit from cms.form.search to add a form for your model. Quick example for partner:
class PartnerSearchForm(models.AbstractModel):
"""Partner model search form."""
_name = 'cms.form.search.res.partner'
_inherit = 'cms.form.search'
_form_model = 'res.partner'
_form_model_fields = ('name', 'country_id', )
_form_fields_order = ('country_id', 'name', )
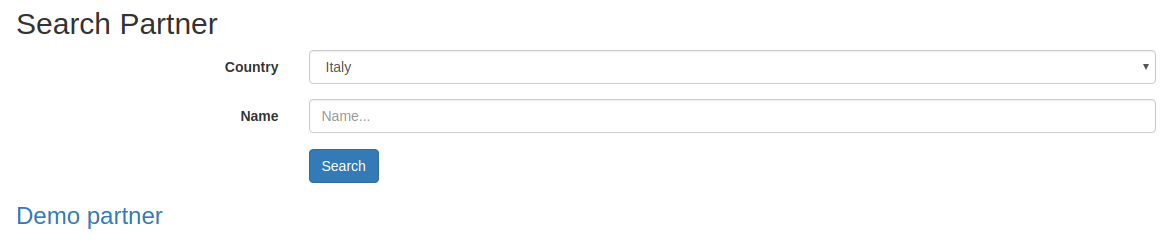
The form will be automatically available at: /cms/search/res.partner.
NOTE: default generic routes work if the form’s name is `cms.form.search + model name, like cms.form.search.res.partner.
If you want you can easily define your own controller and give your form a different name,
and have more elegant routes like /partners.
Take a look at cms_form_example.
Master / slave fields¶
A typical use case nowadays: you want to show/hide fields based on other fields’ values. For the simplest cases you don’t have to write a single line of JS. You can do it like this:
class PartnerForm(models.AbstractModel):
_name = 'cms.form.res.partner'
_inherit = 'cms.form'
_form_model = 'res.partner'
_form_model_fields = ('name', 'type', 'foo')
def _form_master_slave_info(self):
info = self._super._form_master_slave_info()
info.update({
# master field
'type':{
# actions
'hide': {
# slave field: action values
'foo': ('contact', ),
},
'show': {
'foo': ('address', 'invoice', ),
}
},
})
return info
Here we declared that:
- when type field is equal to contact -> hide foo field
- when type field is equal to address or invoice -> show foo field